- Teacher: Kanda 254
kanda254 school of construction
-
Welcome to your new Gnomio site
Now, you are in control!
Moodle is an open-source Learning Management System (LMS) that provides educators with the tools and features to create and manage online courses. It allows educators to organize course materials, create quizzes and assignments, host discussion forums, and track student progress. Moodle is highly flexible and can be customized to meet the specific needs of different institutions and learning environments.
Moodle supports both synchronous and asynchronous learning environments, enabling educators to host live webinars, video conferences, and chat sessions, as well as providing a variety of tools that support self-paced learning, including videos, interactive quizzes, and discussion forums. The platform also integrates with other tools and systems, such as Google Apps and plagiarism detection software, to provide a seamless learning experience.
Moodle is widely used in educational institutions, including universities, K-12 schools, and corporate training programs. It is well-suited to online and blended learning environments and distance education programs. Additionally, Moodle's accessibility features make it a popular choice for learners with disabilities, ensuring that courses are inclusive and accessible to all learners.
The Moodle community is an active group of users, developers, and educators who contribute to the platform's development and improvement. The community provides support, resources, and documentation for users, as well as a forum for sharing ideas and best practices. Moodle releases regular updates and improvements, ensuring that the platform remains up-to-date with the latest technologies and best practices.
Links of interest:
(You can edit or remove this text)
Available courses
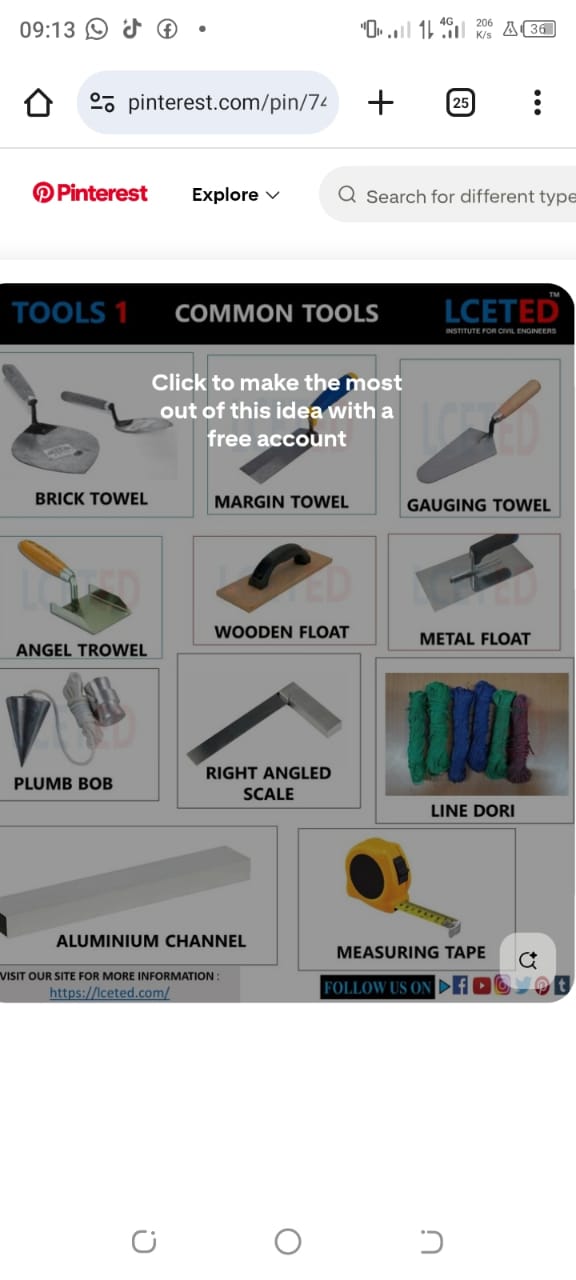
This unit describes the competences required to perform building finishes. It entails plastering building walls (internal and external) applying floor finishes, painting building surfaces, applying building facings, wall mastering, lining wall surfaces, carrying out pointing and jointing, cladding building walls and performing rough cast.